Ransomware is a type of malware designed to perform extortion using an organization's sensitive and valuable data. Originally, this involved encrypting this data and demanding a ransom for the key needed to decrypt and regain access. However, some ransomware groups have recently adapted their tactics to focus on data theft extortion, threatening the exposure of sensitive data unless a ransom is paid.
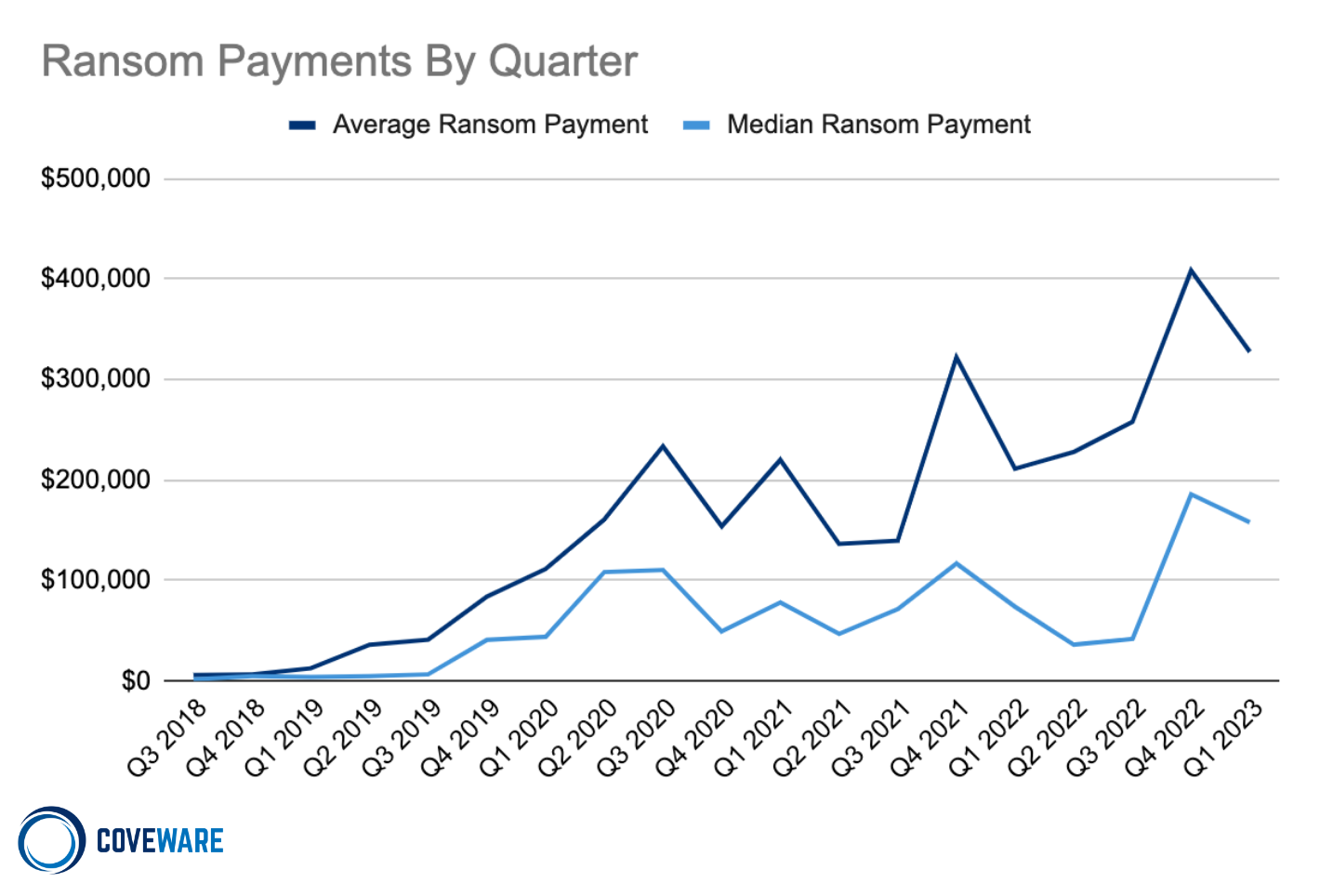
Ransomware has proven a highly successful attack vector for cybercriminals, and ransomware groups are constantly working to define their tactics and malware. Understanding the latest ransomware trends is essential to protecting against attacks, with an average ransom demand of $327,883 in Q1 2023.
Big Game Hunting is back despite decreasing Ransom Payment Amounts
Midway through Q1, the winds of progress shifted, and we observed a material increase in attacks on large enterprises that achieved levels of impact that we had not observed before the Colonial Pipeline attack in May 2021.
Top Ransomware Attacks of 2023
Hundreds of publicly reported ransomware attacks occur each month, and the number of unreported ones is likely much higher. However, some attacks stand out from the rest due to their scope, price, tag, and impacts. Some of the most impactful ransomware attacks of 2023 to date include:
- Royal Mail: The UK’s Royal Mail — which is considered critical infrastructure — suffered a ransomware attack by LockBit in January 2023. The attack disrupted the ability to send letters and packages overseas, causing significant disruption to the organization and many UK citizens.
- New York City Bar: An attack by the Cl0p ransomware group announced in January 2023 included an estimated 1.8 TB of data stolen from the New York City Bar Association. The ransomware group leaked images of file directories stolen during the attack.
- ION: ION — a financial services trading firm with many large banks, hedge funds, and brokerages as clients — disclosed a ransomware attack in February 2023. A ransom was paid to LockBit by an undisclosed party.
- US Marshals Service (USMS): A February 2023 ransomware attack involved the theft of law enforcement data, including employees’ PII and information regarding USMS investigations. A statement claimed that it took roughly 30 days to restore critical tools after the breach was discovered.
- Maximum Industries: Maximum Industries — a company that manufactures parts for SpaceX — reported a data breach in March 2023. The LockBit gang claimed to have stolen 3,000 schematics and blueprints as part of the attack.
- Western Digital: In April 2023, Western Digital disclosed a security incident in which 10 TB of data was stolen, including private keys used for code signing. The BlackCat ransomware group demanded an 8-figure sum to prevent it from being released.
Ransomware attacks use various techniques to access target environments and deploy their malware. In 2023, some of the leading techniques are phishing attacks, compromised user accounts, remote access solutions, and exploitation of vulnerabilities.

Emerging Trends in Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is an effective and profitable Attack method for cybercriminals. One of the reasons for this success is that ransomware groups are continually working to improve their attacks' profitability and success rates.
As a result of this constant innovation, the ransomware threat has evolved significantly over the past few years. Some of the major trends in ransomware attacks include:
- Double Extortion: Originally, ransomware only encrypted data, making backups an effective defense against ransomware. Double extortion attacks incorporate data theft and the threat of sensitive data exposure to force victims to pay the ransom.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Every organization has trust relationships with third parties, including vendors, partners, and software and service providers. Supply chain attacks exploit one organization and take advantage of these trust relationships to gain access to other organizations as well, increasing the impact of the attack.
- Ransomware as a Service (RaaS): Malware development is a specialized skill, and many more cybercriminal groups have the ability to exploit organizations than to write complex malware. RaaS groups operate under an affiliate model where the ransomware group provides other groups with a copy of their malware in exchange for a cut of any ransom earned from it. RaaS dramatically increases the scale and sophistication of the ransomware threat.
- Automated Attacks: As ransomware groups refine their tactics, they increasingly automate their attacks. As a result, ransomware attacks are faster, more sophisticated, and more scalable than ever before.
- Attacks on Critical Infrastructure: In the past, ransomware groups primarily targeted private sector companies. In recent years, attacks have increasingly targeted critical infrastructure, amplifying the impact and disruptions of these attacks.
- Smaller Targets: Previously, ransomware mainly targeted large organizations because their ability to pay large ransoms made the attacks profitable. Today, RaaS, automation, and similar factors have enabled these groups to turn a profit while targeting smaller companies and even individuals.
Future Outlook for Ransomware
Ransomware operators will continue to innovate and carry out their attacks using evolving methodologies.
Ransomware attacks have been highly profitable for cybercriminals, and their continued success indicates that many organizations still lack effective protection against ransomware attacks.
Some of the ways that organizations and individuals can protect themselves against the ransomware threat include the following:
- Secure Backups: Some ransomware groups are moving away from data encryption, but it is still a major threat. Creating regular backups and protecting them from encryption can help reduce the potential impact of a ransomware attack.
- Anti-Ransomware Solutions: Ransomware malware has a common method of operation, including accessing, encrypting, and exfiltrating files. Anti-ransomware solutions can help to identify and halt data encryption and exfiltration, reducing the impact of a ransomware infection.
- Phishing Prevention: Phishing emails are one of the most common methods for ransomware delivery. Email scanning solutions and employee education can help reduce the probability of a ransomware infection.
- Account Security: Compromised accounts are another common tool for ransomware attackers. Implementing strong authentication — including multi-factor authentication (MFA) — and limiting risk via zero trust and least privilege access controls can help to reduce the probability of infection.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Ransomware groups are increasingly transitioning to data theft and extortion attacks. DLP solutions that detect and block the exfiltration of sensitive data can aid in detecting and remediating these ransomware infections.
Stay Aware of Ransomware
Ransomware is an ongoing and evolving threat to corporate cybersecurity. A successful attack can cause operational disruptions, data loss, reputational damage, legal fees, and various other impacts on an organization. For this reason, ransom demands — which typically average in the hundreds of thousands — are only a fraction of the cost of a successful ransomware attack.
Recap of the key points discussed in the article:
Ransomware is an evolving threat, with everything from the major players to the attack vectors changing over time. The best way to manage the ransomware threat is to stay aware of the latest changes in the ransomware threat landscape and ensure that your organization has solutions in place to address them.